In a world dominated by digital technologies and data-driven procedures, the necessity for a strong and adaptable identification system is glaringly apparent. Within the context of India, the Aadhaar Card stands out as an inventive response to this urgent requirement. Conceived by the Unique Identification Authority of India (UIDAI), this 12-digit unique identity number has rapidly integrated itself into India’s socio-economic landscape. In this discourse, we will delve into the manifold applications and extensive advantages of the Aadhaar Card, shedding light on its significant impact on India’s operational ecosystem.
Uses and Benefits of an Aadhaar Card
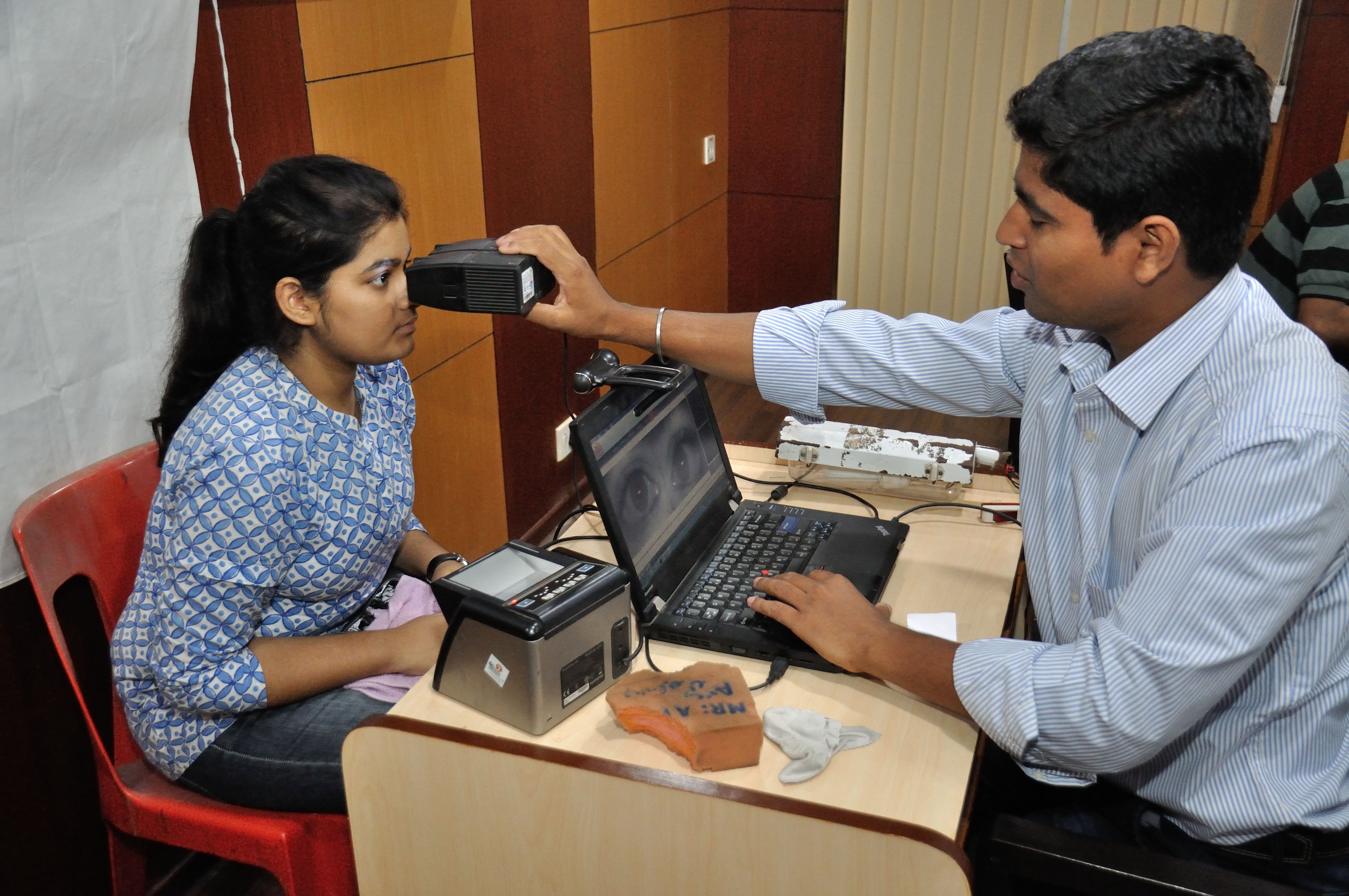
I. Identity Verification
1.1 Enrolment Process
The Aadhaar Card’s chief objective is to establish a singular and supremely secure means of verifying individual identities. Throughout the enrolment procedure, an individual’s demographic details and biometric data, encompassing fingerprints and iris scans, are meticulously gathered. This information is subsequently employed to produce a distinctive Aadhaar number, offering a strong confirmation of one’s identity.
1.2 Linking with Various Services
One of the core benefits of an Aadhaar Card is its extensive linkage with various government services and schemes. It acts as a single-point authentication for accessing services like government subsidies, pensions, and welfare programs, thereby eliminating the need for multiple documents to prove identity and eligibility.

II. Financial Inclusion
2.1 Bank Account Linkage
Aadhaar is a cornerstone of promoting financial inclusivity in India. Through the Jan Dhan Yojana program, the government has actively promoted the establishment of bank accounts for every Indian. The Aadhaar Card streamlines this procedure, simplifying the task of opening and managing bank accounts, facilitating the receipt of government subsidies, and granting access to a wide array of financial services.
2.2 Direct Benefit Transfer (DBT)
The Aadhaar Card has revolutionized the distribution of government subsidies and benefits through the Direct Benefit Transfer (DBT) system. By linking bank accounts with Aadhaar, subsidies are transferred directly, reducing corruption and ensuring that the intended beneficiaries receive their entitlements promptly.
III. e-Governance
3.1 Digital India Initiative
The Aadhaar Card serves as a cornerstone in the government’s Digital India campaign, with the goal of revolutionizing the nation into a digitally empowered community. This card facilitates online access to government services, tax return submissions, and the effortless utilization of numerous entitlements by its citizens.
3.2 Paperless Verification
In the past, verifying one’s identity for government services often required a plethora of documents, leading to inefficiency and corruption. Aadhaar enables paperless verification, streamlining the process and reducing the burden on citizens and government officials alike.
IV. Healthcare
4.1 eHealth Records
Linking Aadhaar to healthcare services enables the creation of electronic health records (EHR), streamlining access to a patient’s medical history and enhancing the ability of healthcare providers to deliver precise and prompt care.
4.2 Telemedicine
The COVID-19 pandemic underscored the importance of telemedicine. By sharing their Aadhaar details, patients can easily connect with healthcare providers online, ensuring quick access to medical advice and consultations.
V. Education
5.1 School Admissions
Aadhaar Cards simplify the process of school admissions. They serve as a reliable proof of identity, making it easier for children to enroll in educational institutions.
5.2 Scholarship Distribution
For students seeking scholarships and financial assistance, Aadhaar ensures a streamlined process for the disbursement of funds. This helps students receive the support they need to pursue their education.
VI. Digital Verification
6.1 Mobile SIM Verification
The Aadhaar Card is required for mobile SIM card verification, enhancing security and preventing the misuse of mobile numbers for fraudulent activities.
6.2 Online Transactions
With Aadhaar-linked bank accounts, online transactions have become more secure and convenient. It is also instrumental in preventing identity theft and fraud in the digital space.
VII. Property and Legal Transactions
7.1 Property Ownership
Aadhaar Cards can be used to verify property ownership, simplifying the process of buying, selling, or transferring property. This significantly reduces fraudulent land deals.
7.2 Legal Documentation
Aadhaar serves as a valid proof of identity in legal documentation and court proceedings. It streamlines the process, making it more efficient and accessible for citizens.
VIII. Social Inclusion
8.1 Targeted Welfare Programs
The Aadhaar Card enables the government to target welfare programs to those who need them the most, ensuring that vulnerable populations receive the assistance they require.
8.2 Empowering the Underprivileged
The Aadhaar Card empowers the underprivileged by providing them with a valid identification, which is often the first step towards accessing government schemes and services.
Conclusion
The Aadhaar Card’s profound impact on India’s administrative framework has ushered in a multitude of advantages for its populace. Covering aspects like identity authentication, financial access, electronic governance, healthcare, education, and social welfare, it has imprinted an enduring influence on all sectors of Indian life. Through its versatile array of applications and strong security measures, the Aadhaar Card remains a driving force in propelling India towards a future marked by inclusivity, efficiency, and digital empowerment. Its versatile utility and evolving benefits make it an essential instrument for India’s socioeconomic progress.
Read More:- Unveiling the Ultimate Guide: The Best Books for Preparing for the KVPY Exam
Read More:- UNVEILING THE ULTIMATE MEMORIZATION TECHNIQUES FOR VERBAL AND











